Optimizing Boiler Furnace Designs Using CFD and Combustion Simulations
In recent years, demand for improved energy efficiency has grown and there is an increasing need for the solid residue generated during the petroleum refinery process to be used as boiler fuel.
This solid petroleum residue contains very little volatile matter, so ensuring stable mono-fuel combustion using this residue is difficult. The residue also contains a lot of ash with a high vanadium content, which has a negative effect on the boiler performance.
KHI has successfully conducted low-NOx and low-dust combustion for liquid petroleum residue by using a structure that combines two combustion chambers, with the low-temperature oxidization zone in the top chamber and the high-temperature reduction zone in the bottom chamber. When asphalt pitch or other solid residues containing ash were used, however, ash accumulating at the bottom of the boiler furnace proved problematic as it made the long-term continuous operation of the boiler more difficult.
To overcome this problem, we developed the U-KACC* boiler, which reverses the positions of the two combustion chambers to allow the ash to be discharged from the hopper at the bottom of the boiler furnace.
During the development of this new boiler, we used numerical simulation technologies to ascertain the combustion conditions of asphalt pitch, the temperature distribution in the furnace and the behavior of the fuel particles.
* U-KACC : Upgraded- Kawasaki Advanced Clean Combustion

Asphalt pitch-fired U-KACC boiler
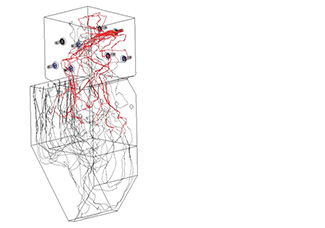
Simulation of fuel particle behavior





