Clean Combustion
Technologies for reducing the quantity of hazardous materials generated by the combustion of fuel or waste.
Waste to Energy Technology
Modern municipal solid waste treatment plants not only reduce the environment load, but also effectively recover the waste heat from incineration as energy. As a result, power generation facilities are generally installed at these plant.
In response to such social needs, KHI has developed and released a next-generation stoker-type incinerator: the Kawasaki Advanced Stoker System.
To reduce the quantity of hazardous materials contained in the exhaust gas produced during the incineration process, the waste must be completely combusted at a high temperature.
Consequently, we have introduced the parallel flow type incinerator. This device makes it possible to perform either incineration at a low air ratio or complete incineration at a high temperature by carrying out the turbulent mixing of unburnt gas and unused oxygen effectively with secondary air.

Panoramic view of the waste to energy plant
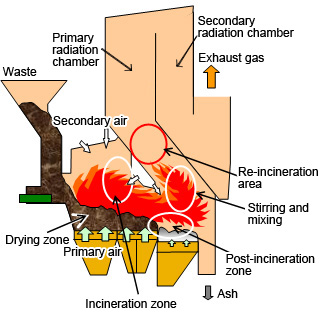
Kawasaki Advanced Stoker System: Parallel flow type incinerator
Petroleum 02Residual Combustion Boiler Technology
After gasoline is derived from petroleum, heavy oil and other residual petroleum products remain. In recent years, the demand for effective use of this heavy oil and other products as fuel is growing.
Since petroleum residual oil contains a lot of nitrogen, it could not be used in boilers because of the large amount of NOx that was emitted during combustion. But now, we have developed the Kawasaki Advanced Clean Combustion (KACC) boiler and realized stable low-NOx combustion of petroleum residual oil.
Furthermore, we are currently developing the U-KACC (Upgraded KACC) boiler, which can combust difficult-to-burn petroleum cokes, without using an auxiliary fuel such as natural gas.

Ultra-low NOx petroleum residual combustion boiler (KACC)
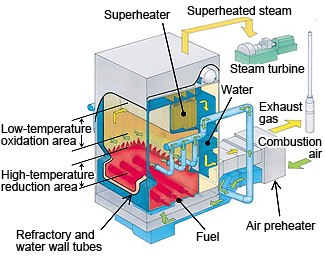
Structure of the KACC boiler





