Waste FREE (Realization of a Recycling-oriented Society)
- Our Basic Stance
- The Environmental Management Activities Plan (Waste FREE)
- Effective Use of Resources
- Conservation of Water Resources
Our Basic Stance
At a time when global population growth is expected to require resources equivalent to 2 earths by 2030, there is a growing public demand to reduce the use of natural resources and reduce waste emissions in order to make society sustainable. The Kawasaki Group is forwarding initiatives aimed at realizing a recycling-oriented society while promoting the effective use of its finite resources by reducing the amount of resources used, reducing waste in the manufacturing process, and recycling waste. In terms of water resources, we are also working to reduce water usage by understanding the state of water use at individual plants and studying ways to use water effectively without waste, thereby reducing our impact on the environment.
The Environmental Management Activities Plan (Waste FREE)
The Environmental Management Activities Plan 2024 (Key Strategies) and Achievements in Fiscal 2024
| Key Strategies of the Environmental Plan 2024 | Achievements in Fiscal 2024 |
|---|---|
| (a) Resource and water cycles | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (b) Enhancing data compilation and capacity to disseminate information | |
|
|
|
|
The Environmental Management Activities Plan 2025
(Key Strategies)
| Key Strategies of the Environmental Plan 2025 | |
|---|---|
| (a) Resource and water cycles
Scope of application: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, and Kawasaki Motors
|
|
(b) Enhancing data compilation and capacity to disseminate information
|
|
Effective Use of Resources
Reducing Resource Consumption
To reduce our burden on the environment, in each stage of product planning, R&D, and design, we are engaged in efforts to make our use of resources more efficient by doing things such as reducing the number of parts and making them lighter, in order to reduce our use of natural resources. In addition to resources used in the manufacture of products, we are reducing the resources used in the packaging of products by expanding the application of returnable shipping trestles and transitioning to packaging materials with lower environmental impacts. As efforts to reduce the use of natural resources are an issue to be worked on by not only the Group but also throughout our entire supply chain, we have incorporated a statement on minimizing the use of natural resources into Kawasaki Group Sustainable Procurement Guidelines and will advance our efforts with our suppliers.
Reducing Waste in Manufacturing Processes
We are continuing efforts with the target of reducing our direct-to-landfill waste to zero by reducing waste through the efficient use of resources in manufacturing processes and promoting the recycling of waste produced in manufacturing processes. The total waste emissions for the Kawasaki Group over the past four years as well as the amount of waste and hazardous waste for Kawasaki Heavy Industries are indicated on the ESG data page. The landfill disposal rate (= direct-to-landfill waste generation ÷ total waste generation) for Kawasaki Heavy Industries in fiscal 2024 was 0.1%, thereby achieving the target of 1% or less set in the Environmental Management Activities Plan 2024. Starting in fiscal 2025, we set a target of reducing the amount of industrial waste generated per unit of sales of Kawasaki Heavy Industries by 1% compared to the previous fiscal year to promote improved resource utilization efficiency and the resulting reduction in waste emissions, and we are conducting appropriate waste management.
Use of Lifecycle Analysis
We carry out product assessments regarding reducing our consumption of natural resources, energy conservation, recycling properties, product safety, and other factors for newly developed/designed products and particularly important products, with the aim of reducing the environmental burden of our products throughout the product lifecycle. As the specific evaluation method differs depending on the product type, all business segments create Product Assessment Rules specific to the types of products in each business to enable the implementation of assessments tailored to the characteristics of each product. The main evaluation items are as follows:
- Weight reduction of the product
- Weight reduction of product packaging materials
- Improved energy conservation at the time of manufacturing the product
- Improved energy conservation when using the product
- Increased lifespan of the product
- Safety and environmental friendliness of the product
- Harmfulness and toxicity of substances contained in products
- Ease of product transport operations
- Environmental impact of packaging and transportation
- Action for the disposal and recycling of the product
- Environmental impact in the event of an emergency such as an accident
- Provision of information for usage/maintenance, etc.
- Compliance with laws and regulations
Initiatives for a Circular Economy
Participation in Partnership of Industry, Government, and Academia on Circular Economy
Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. announced on August 2024 that it has participated in the partnership of industry, government, and academia on circular economy, named “Circular Partners” which is led by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan (METI). In the Kawasaki Group Policy on Environmental Management established in June 2024, the Company has stated that it will contribute to a sustainable society through technologies, products, and services, and our efforts for a circular economy are one of our activities that follow this policy. In the future, the Company will implement circular economy initiatives in relation to each product of the Kawasaki Group. The Company will promote the development of environmentally conscious products with consideration for longevity, degradability, and recyclability on the product design stage. In particular, the Company will promote the effective use of recycled resources by increasing the ratio of recycled materials in raw materials used during manufacturing process and promoting the use of recycled materials in products and their parts. In addition, through our participation in Circular Partners, the Company will contribute to the realization of a sustainable society in resource recycling throughout the supply chain by actively collaborating with external stakeholders in the use of precedents and joint research.
Goals in the Partnership between Industries, Academia, and Government on Circular Economy
The Company submitted its initiative goals for Circular Partners in August 2025. The details of the goal submitted by the Company are shown in the table below. We will continue our efforts to create technologies and solutions for achieving a recycling-oriented society by leveraging our proprietary technologies in energy equipment, hydraulic pumps, railway vehicles, robots, plants, and other areas and making use of partnerships of industry, government, and academia as well as open innovation.
| Goals | Number of initiatives | Achievement period |
|---|---|---|
| Initiatives toward realizing a circular society including reduction of hazardous substances, use of recycled materials, improvement of manufacturing processes, and provision of solutions | 6 | By Dec. 31, 2030 |
Motorcycle Recycling System
Kawasaki Motors, Ltd. participates in the Motorcycle Recycling System, a voluntary initiative which has been jointly operated by Japanese motorcycle manufacturers and importers since 2004. The actual recycling rate for fiscal 2024 as part of this Motorcycle Recycling System was 97.8%. Since October 2011, we have also made recycling free of charge (excluding transport costs) for customers disposing of their motorcycles. Additionally, we are engaged in initiatives for the environmentally conscious design of new motorcycle models, including reduce and recycle initiatives, from the development stage. We meanwhile conduct preemptive assessments of 3R initiatives in advance of the design, prototyping, and mass production stages. We have particularly endeavored to improve recyclability through measures including the adoption of easily recyclable materials. Our recyclability rate, calculated in accordance with the “Guidelines for the Definition and Calculation Method on the Recyclability Rate for New Vehicles (JAMA 1998)” issued by the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association, Inc. (JAMA) is 90% or more for all models, with the majority of models having achieved a recyclability rate of 95% or more.
Promoting PCB Treatment
The disposal of PCB (polychlorinated biphenyl) waste is proceeding worldwide, in line with the Stockholm Convention, which includes stipulations on the proper treatment of PCBs. In Japan, disposal is undertaken in a systematic manner, mainly by the Japan Environmental Storage & Safety Corporation (JESCO), which was established by the Ministry of the Environment. The phased disposal period for high-concentration PCB waste is scheduled to end in 2023, and that for low-concentration PCB waste will end in 2027. The Group is implementing scheduled disposal of PCB waste and has completed the disposal of high-concentration PCB waste. For the remaining low-concentration PCB waste, we will re-investigate the target materials and proceed with proper disposal for completion at the end of the disposal period in 2027.
Conservation of Water Resources
Precisely Understanding Water Uses and Usage Volumes
To more effectively use water resources, Kawasaki Heavy Industries is advancing efforts to precisely understand water usage at each of their plants. In addition, we are monitoring wastewater discharge by setting voluntary control standards for wastewater discharged from plants, with these standards more stringent than discharge standards under laws and ordinances, with Kawasaki thereby working to improve wastewater quality. Water withdrawal, water discharged, and water consumed at Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, and Kawasaki Motors over the last four years are shown on the ESG data page. In fiscal 2025, to encourage reduced usage by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, and Kawasaki Motors we set a target of reducing water withdrawal per unit of sales by 1% compared to the previous fiscal year and have been working to reduce water consumption by reconfirming the use of water in production activities and boiler use and by investigating effective use without waste, using recycled water, and other measures. By rolling out these initiatives across the Group, we will reduce water resource risks.
Manufacturing Facilities and Water Level Risk (Water Stress)
In collaboration with external experts, we conducted a simple risk analysis from the perspectives of water shortage, drought, flooding, and water pollution utilizing the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas published by U.S. think tank WRI (World Resources Institute). Of the 38 manufacturing facilities we have in Japan and overseas (17 in Japan, 21 overseas), we have 12 manufacturing facilities in India, Thailand, and China, where water stress is seen to be high compared to other countries around the world. Seven of these facilities were determined to be at particularly high risk of water resources and drought. Going forward, we will implement more detailed analyses and actively institute measures to address any issues.
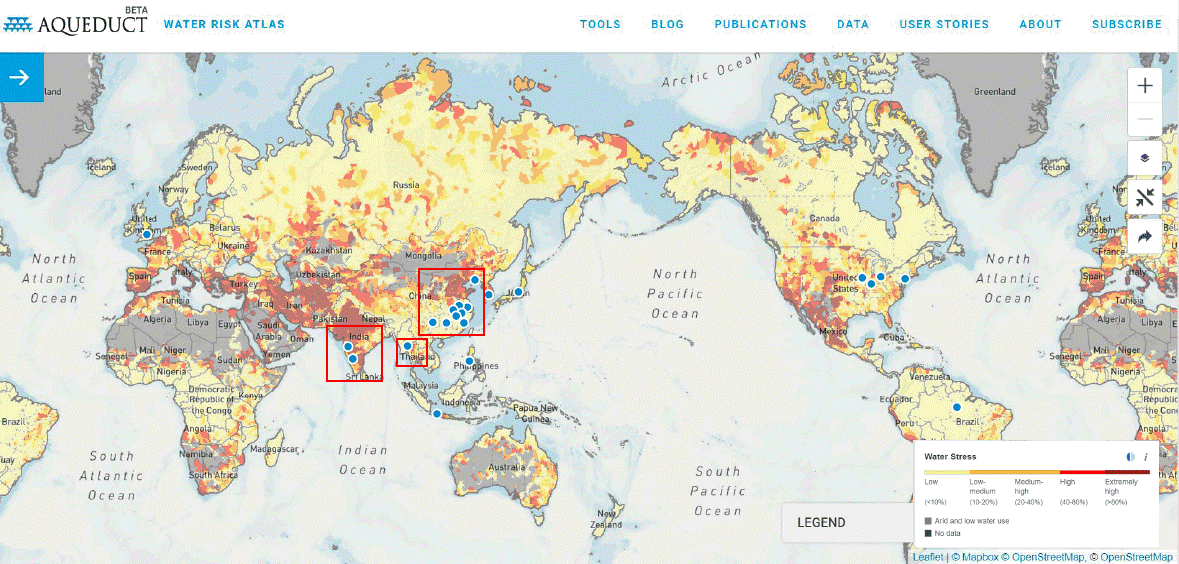
Legend
●:Kawasaki Group's
manufacturing facilities
□:Countries and regions with particularly high water stress
Contact
If you need more information about our business,
please feel free to contact us.





