CO2 FREE (Realization of a Carbon-neutral Society)
- Carbon Neutrality Targets
- Information Disclosure in Line with the TCFD Recommendations (Scenario Analysis)
- Environmental Management Activities Plan (Short-term Target and Plan)
- External Affairs Activities Concerning Climate Change
Our Basic Stance
In October 2020, the Japanese government declared its target of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, to this end raising its fiscal 2030 reduction target for CO2 emissions from 26% to 46% (both compared with the fiscal 2013 level) in April 2021. This is but one example of decisions made by countries around the globe amid the accelerating trend toward across-the-board decarbonization and the realization of a low-carbon society. Toward achieving the CO2-free target set out in the Kawasaki Global Environmental Vision 2050, the Kawasaki Group is not only actively engaged in realizing carbon neutrality at its plants (Scope 1 and 2) but also throughout its supply chain (Scope 3).
Carbon Neutrality Targets
The Kawasaki Group aims to realize the objective set down in the Paris Agreement of limiting the increase in the average global temperature to 1.5ºC above pre-industrial levels. Under Group Vision 2030, we aim to achieve carbon neutrality at the Group and our domestic consolidated subsidiaries by 2030 through the further advance of energy saving, the introduction and expanded use of renewable energies, and the expansion of waste-to-energy power generation, as well as independent initiatives focusing on hydrogen power generation.* Furthermore, we will expand the Group’s decarbonization solutions to society, our business partners, and our customers, contributing to the early achievement of carbon neutrality around the world. Toward that end, we are dealing with many products and services essential to transition from fossil fuels to carbon neutrality, such as highly efficient power generation equipment and gas turbines for mixed firing with hydrogen, and will thereby make significant contributions in this fields as well.
* We are reviewing the timing for achieving carbon neutrality, taking into account the recent trend toward a return to LNG in energy markets and the circumstances of our main partners.
| Reference Website |
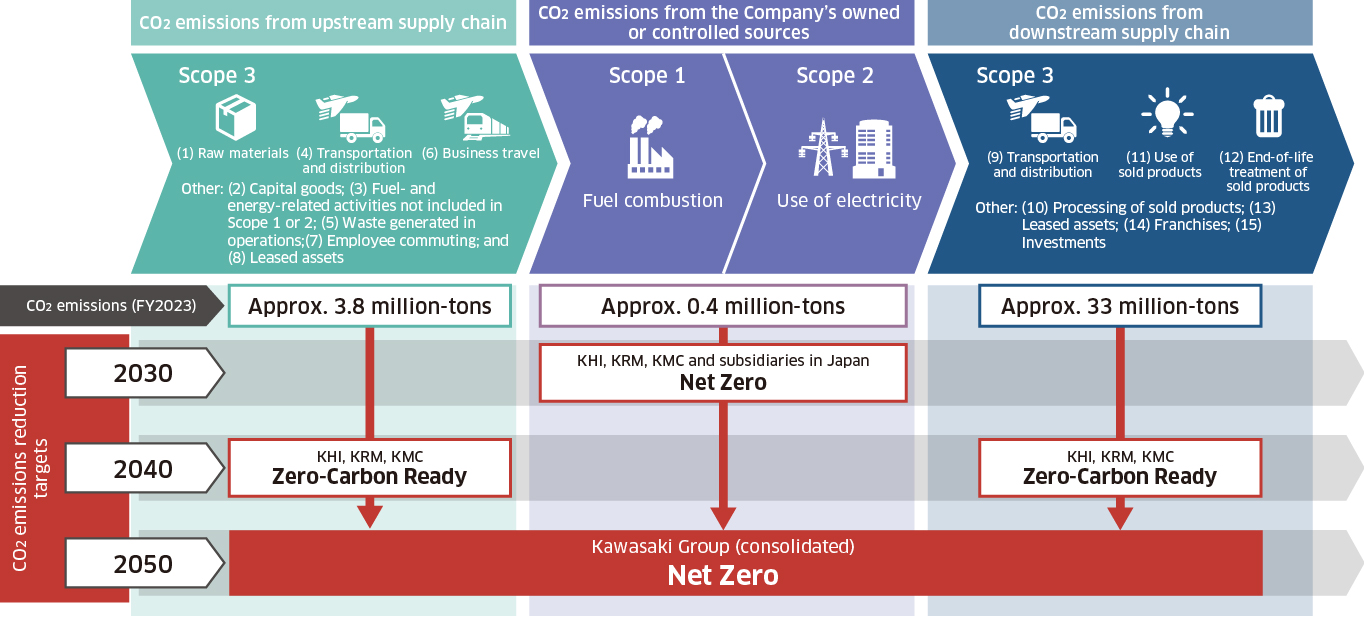
Scope 1 and 2
Corresponding companies: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, Kawasaki Motors + Affiliated companies in Japan
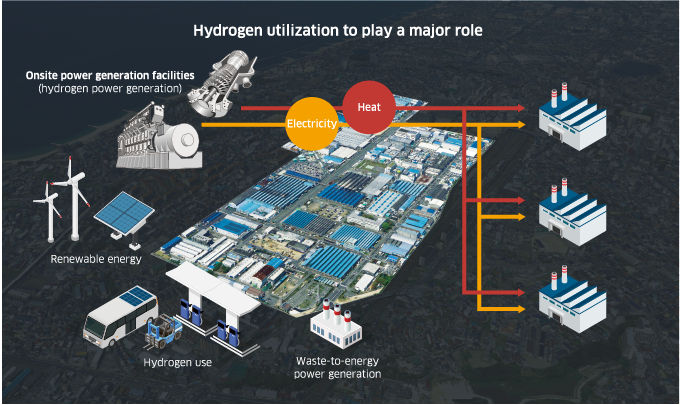
Toward the Realization of Carbon Neutrality in the domestic Group by 2030 through Initiatives Focusing on Hydrogen Power Generation
As shown to the right, the Kawasaki Group’s Scope 1 and 2 CO2 emissions are approximately 400,000 tons annually, of which Japan account for three-quarters. We will continue efforts to save even more energy and promote electrification and the use of sustainable energy, such as solar power generation, to reduce CO2 emissions. We will also introduce in-house hydrogen-fueled power generation facilities and achieve zero-emissions plants by combining this with power generation from waste, renewable energy, and other energy sources. Through these initiatives, we plan to achieve independent carbon neutrality with zero CO2 emissions by the Group in Japan. We are also working to reduce CO2 emissions overseas.*
* We are reviewing the timing for achieving carbon neutrality, taking into account the recent trend toward a return to LNG in energy markets and the circumstances of our main partners.
CO2 Emissions Reduction Plan in Japan
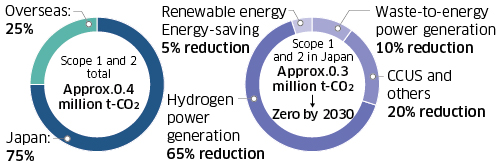
Zero-Emissions Plant
Zero-emissions plant refers to initiatives to achieve zero CO2 emissions from plants by obtaining the electricity and thermal energy used at the plants from a combination of methods that do not emit any CO2, such as hydrogen power generation, solar power generation, and waste power generation. The Kawasaki Group will reduce CO2 emissions throughout the Group by converting its plants in Japan to zero-emissions plants.
CO2 emissions and reduction targets (Scope 1 and 2)

Scope 3
Corresponding companies: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, Kawasaki Motors
Leading Society by Advancing Toward Zero-Carbon Ready
Scope 3 Net Zero can only be achieved when all parties in the value chain including trading partners and clients become Zero-Carbon Ready. The Company will implement the maximum possible measures concerning Scope 3 to become Zero-Carbon Ready by 2040. Specifically, for category (i), we will slash CO2 emissions by suppliers of materials and parts by 80% compared to fiscal 2021, and for category (xi), we will develop a lineup of CO2-free standard solutions in all businesses. Moreover, we will reduce CO2 emissions by more than the Company’s own Scope 3 emissions by working toward achieving a hydrogen-based society and engaging in the CCUS business, thereby contributing to the early achievement of carbon neutrality around the world.
Scope 3 Breakdown by Categories
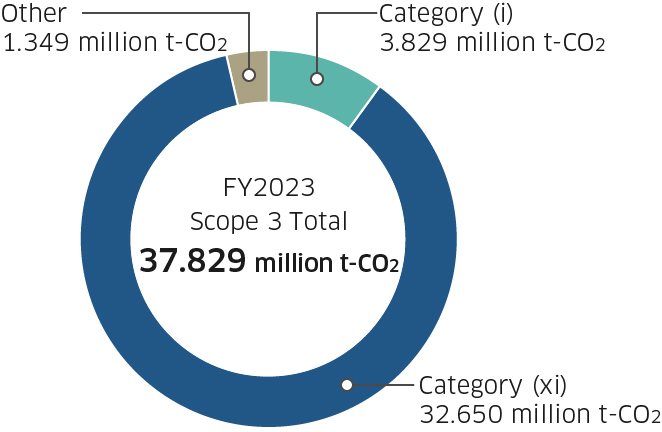

CO2 emissions and reduction targets (Scope 3)

Scope 3 Category (i) Procurement of materials and parts
Support Industrial Initiatives with Hydrogen and CCUS Solutions to Further Accelerate Reductions
The Company will deepen its partnerships, including sharing emissions data with business partners that supply materials and parts, offering support for CO2 reductions and striving for early achievement of zero emissions. This will be achieved by means not limited to in-company utilization by the Group of solutions such as hydrogen power, hydrogen fuel, and other alternative fuels, as well as CCUS, but also by providing these solutions to business partners. When reducing CO2 emissions from purchased goods, we strive to collaborate with suppliers on reducing emissions. In April 2024, we held a briefing on carbon neutrality and provided a summary of the Kawasaki Group’s initiatives and guidelines toward the realization of a carbon-neutral society while requesting that suppliers also make efforts to reduce CO2 emissions. Additionally, starting in fiscal 2024, we have been conducting carbon neutrality seminars, mainly for business partners, and provide support to major business partners regarding CO2 emission calculations and emission reduction initiatives intended to improve the primary data ratio for Scope 3 Category (i) CO2 emissions. We will expand these types of initiatives companywide in the future and build further collaborative structures with business partners to reduce emissions.
|
Scope 3 Category (i) (CO2 reductions scenarios)

Scope 3 Category (xi) Providing customer solutions
Provide CO2-free Solutions to All Customers
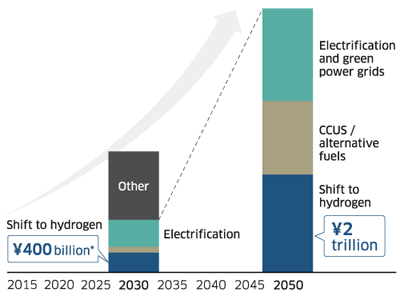
We will take action to decarbonize products and services with hydrogenation, electrification, green power grids, alternative fuels, and CCUS as our keywords. In the short-term initiatives toward 2030, through Kawasaki Ecological Frontiers, a program for certification of environmentally friendly products, and other initiatives, we will continue to reduce the energy consumption and improve the efficiency of existing products and promote the shift to hybrid electric and battery electric motorcycles and other vehicles as part of the transition to a decarbonized society. We will also conduct development for the commercialization of hydrogen energy and expand the use of hydrogen in gas turbines, gas engines, and other equipment. Furthermore, we will work toward the development of Kawasaki CO2 Capture and DAC for the capture and use of CO2. In medium- to long-term initiatives toward 2040, the Group will actively further the following three major initiatives. The first will be the provision of CO2-free fuels and electrical power to society, with a focus on its hydrogen business. The second will be to make a selection of choices for electrification and CO2-free fuels available to customers utilizing our various solutions including mobility and robots. The third will be promoting CO2 capture as well as the effective use of CO2 including the manufacture of synthetic fuels and chemical products to achieve a circular CO2 society. With these three pillars, the Group will make choices available to our customers of products and services (excluding defense and related; emergency products business) that contribute to the achievement of carbon neutrality by 2040, and promote global reductions in CO2.
* From fiscal 2021, the Group modified its calculation method to allow more accurate records of emissions levels for Scope3 category (xi). Previously, CO2 emissions levels for products such as hydraulic machinery, manufactured as parts to be incorporated in finished products, were calculated by tallying the CO2 emissions levels of the finished products such as construction machinery. However, from fiscal 2021, these calculations will also take into account the degree of contributions and weight ratios for final products.
Envisioned Scale of Business by Future Solution
Information Disclosure in Line with the TCFD Recommendations (Scenario Analysis)
Climate change-related information based on TCFD recommendations is reported in the Kawasaki Report. Please refer to the link below for the details on our report after fiscal 2023.
Environmental Management Activities Plan (Short-term Target and Plan)
Aiming to achieve its carbon neutrality target, while the Company will step up efforts to introduce in-house hydrogen power generation to achieve carbon neutrality at its plants (Scope 1 and 2), it will continue its ongoing efforts to scale the introduction of renewable energy and to save energy. Furthermore, the Company will accelerate these efforts with the introduction of internal carbon pricing. To achieve carbon neutrality in its supply chain (Scope 3), the Company aims to realize Zero-Carbon Ready by 2040 by advancing its provision of CO2-free solutions to its business partners and customers. One aspect of Scope 3 reductions is the public disclosure of CO2 emissions reduction contributions* by products.
* For information on emissions reduction contributions, refer to “Reducing CO2 Emissions through Product-Based Contributions” below on this page.
The Environmental Management Activities Plan 2024
(Key Strategies) and Achievements in Fiscal 2024
| Key Strategies of the Environmental Plan 2024 | Achievements in Fiscal 2024 |
|---|---|
| (a) Reduction of CO2 emissions in entire supply chain | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (b) Expanded introduction of decarbonized energy | |
|
|
|
|
| (c) Fuel conversion | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Environmental Management Activities Plan 2025
(Key Strategies)
| Key Strategies of the Environmental Plan 2025 |
|---|
(a) Reduction of CO2 emissions in entire supply chain
|
(b) Expanded introduction of decarbonized energy
|
(c) Fuel conversion
|
Scope 1 and 2 Efforts
Corresponding companies: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, Kawasaki Motors
Utilizing Renewable Energy
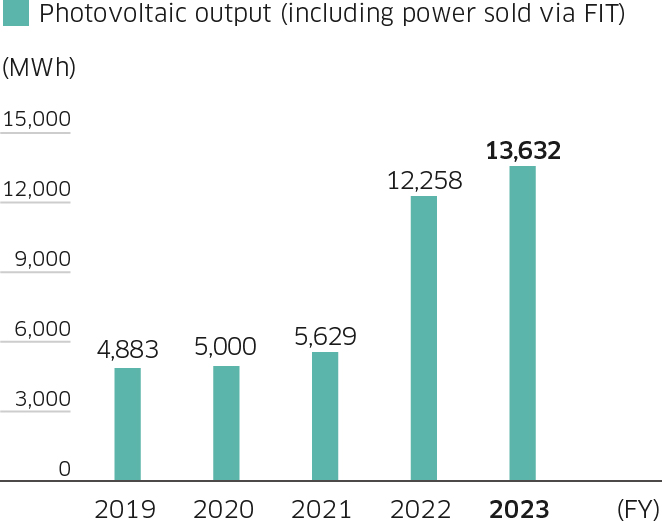
The Kawasaki Group is advancing the use of renewable energy to reduce the CO2 emissions from its plants. To this end, we are installing solar power generating systems at our plants. We have a total solar power generation capacity of 13,534 kW including Group companies. In fiscal 2024, these systems generated 14,826 MWh, of which 11,842 MWh was used in-house. Electric power used in-house is equivalent to 1.75% of the electricity consumed throughout the entire Group.
The Kawasaki Group’s Solar Power Generation Capacity
| Name | Power Usage | Generation Capacity (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| Iwaoka Photovoltaic Power Generation Station1*1 | Sold via FIT*2 | 1,505 |
| Seishin Works | Used in-house via PPA | 1,444 |
| Harima Works | Used in-house via PPA | 783 |
| Nagoya Works 1 | Used in-house | 750 |
| Seishin Photovoltaic Power Generation Station*1 | Sold via FIT | 701 |
| Nishi-Kobe Works | Used in-house | 640 |
| Nishi-Kobe Photovoltaic Power Generation Station*1 | Sold via FIT | 422 |
| Akashi Works | Used in-house | 230 |
| Kakogawa Photovoltaic Power Generation Station*1 | Sold via FIT | 48 |
| Kobe Head Office of Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Used in-house | 25 |
| Kobe Works | Used in-house | 20 |
| EarthTechnica Co., Ltd. | Used in-house | 133 |
| Kawasaki Thermal Engineering Co., Ltd. | Used in-house | 7 |
| Kawasaki Motors Enterprise (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | Used in-house via PPA | 5,000 |
| Kawasaki Precision Machinery (UK) Ltd. | Used in-house | 999 |
| Kawasaki Robotics (Kunshan) Co., Ltd. | Used in-house via PPA | 840 |
| Total | 13,547 | |
- *1 Power generation facility operated by Kawasaki Trading Co., Ltd.
- *2 FIT: Feed-in tariff; a program in which renewable energy is bought back at a fixed rate
Photovoltaic Output (including power sold via FIT)


Systematic Investment in Energy-Saving Equipment
As a measure to promote energy-saving activities, in 2022, the Company introduced an initiative to set reference values for the CO2 reduction efficiency of energy-saving investment projects as criteria for determining the investment in such projects and to increase the equipment budget allocation for projects in which the reduction efficiency meets the criteria. Through this initiative, the Company will continue to reduce its CO2 emissions by advancing its investments in equipment with a focus on projects with a high CO2 reduction efficiency. Such equipment investment projects include upgrading production equipment, switching air conditioning systems to those that run on electricity, and changing to LED lighting. In addition, in accordance with the Act on Rationalization of Energy Use and Shift to Non-fossil Energy, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, and Kawasaki Motors aim to reduce unit energy consumption by an average of 1% per year.
Internal Carbon Pricing
To promote investment in carbon neutrality efforts such as the introduction of future hydrogen equipment and renewable energy and to change behavior within the Company, since fiscal 2022, the Company has introduced internal carbon pricing. Specifically, a carbon surcharge will be imposed in an amount calculated by multiplying the Scope 1 and 2 emissions of Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, and Kawasaki Motors in the previous fiscal year by a CO2 unit price (2000 yen/t-CO2). The aim is to make concentrated investments in carbon neutrality efforts based on the funds generated from surcharges of the internal carbon pricing program.
Energy-Saving and Decarbonization Award System
To achieve our carbon neutrality goals, the Company shares examples of improvement concerning energy savings and decarbonization initiatives with internal companies and affiliated companies. In addition, we operate the Energy-Saving and Decarbonization Award System to help more employees become aware of CO2 emissions reduction and cost reduction. Under this program, we provide incentives (monetary rewards) to employees who achieve outstanding results in reducing CO2 emissions and cutting resource and energy costs at production sites and offices.
Reducing CO2 Emissions through Product-Based Contributions
Corresponding companies: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kawasaki Railcar Manufacturing, Kawasaki Motors
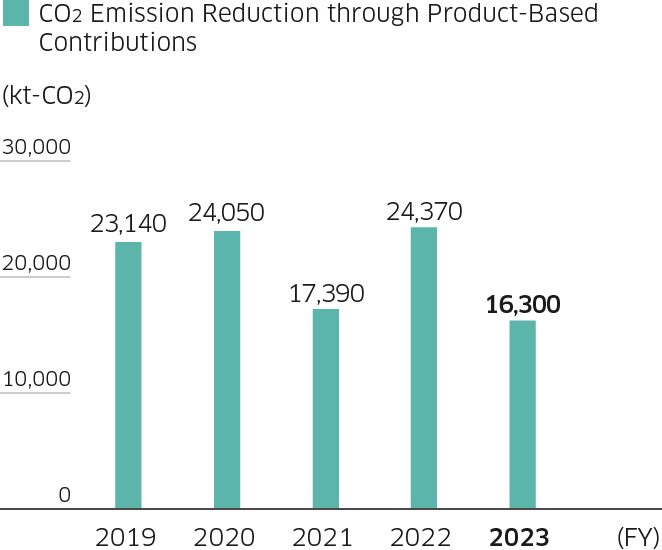
Nearly 90% of CO2 emitted during the life cycles of our products is released during the period of their use after they are sold. Therefore, the Company seeks to realize a carbon-neutral society by providing products that produce only low CO2 emissions during their use. To reduce products’ post-sale CO2 emissions, in addition to increasing product energy efficiency, we are advancing electrification and modal shifts when replacing existing products in our product lineup and expanding our lineup of products that utilize exhaust heat, waste, and renewable energy. Key products that help reduce CO2 emissions are listed below. In fiscal 2017, we revised our rules for calculating CO2 emissions reductions through product-based contributions in order to better quantify the contributions of such products to the mitigation of global warming. Calculations based on these rules showed that the CO2 emissions reduction* through products we sold in fiscal 2024 was about 19.05 million tons. Large contributions were made mainly by the M7A Series gas turbines for power generation, which boast excellent reliability, economy, and environmental friendliness and are certified under the Kawasaki Ecological Frontiers system, an internal certification program for environmentally conscious products, and the KC-MB-20, a controller for use in construction machinery to improve its fuel efficiency via the application of superior controlling technologies.
* Reduction in CO2 emissions compared to earlier products (refer to the calculation rules below.)
Calculation Rules
- Products to be assessed: Kawasaki Ecological Frontiers system, products that use waste, waste heat, and renewable energy, as well as cogeneration systems and rolling stock pertaining to modal shifts, etc., were selected for assessment.
- Period of assessment: We have adopted a flow-based approach* in which the period of assessment is the estimated useful life of products sold in the fiscal year, because the estimated useful lives of our products are long. This allows us to better calculate the difference in CO2 emissions between our products and industry standard class products over the entire period of use.
- The calculation method expressed as a calculation formula is as follows: CO2 emissions through product-based contributions = (annual CO2 emissions from conventional products - annual CO2 emissions from new products) x (assumed number of usage years)
* Please refer to the "Guideline for Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Contribution" (Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, March 2018)
In order to quantify the contributions of highly energy efficient products to the mitigation of global warming, products included in the calculation of CO2 emissions reduction through product-based contributions include power generated through waste heat, waste, renewable energy, and so forth. As a result, some of the products included differ from those included in the calculation of Scope 3, category (xi), which covers only energy-derived CO2 emissions.
CO2 Emission Reduction through Product-Based Contributions
- Notes: 1. Kawasaki uses CO2 emissions factors provided in the list of calculation methods and emissions factors published by Japan’s Ministry of the Environment.
- 2. The CO2 emission reduction effect through product-based contributions achieved through the higher energy efficiency of products is based on a comparison using industry standard products.
- 3. The application of waste heat, waste, and renewable energy is counted toward the CO2 emissions reduction effect through product-based contributions.
Key Products That Contribute to Reducing CO2 Emissions During Use (by Segment)
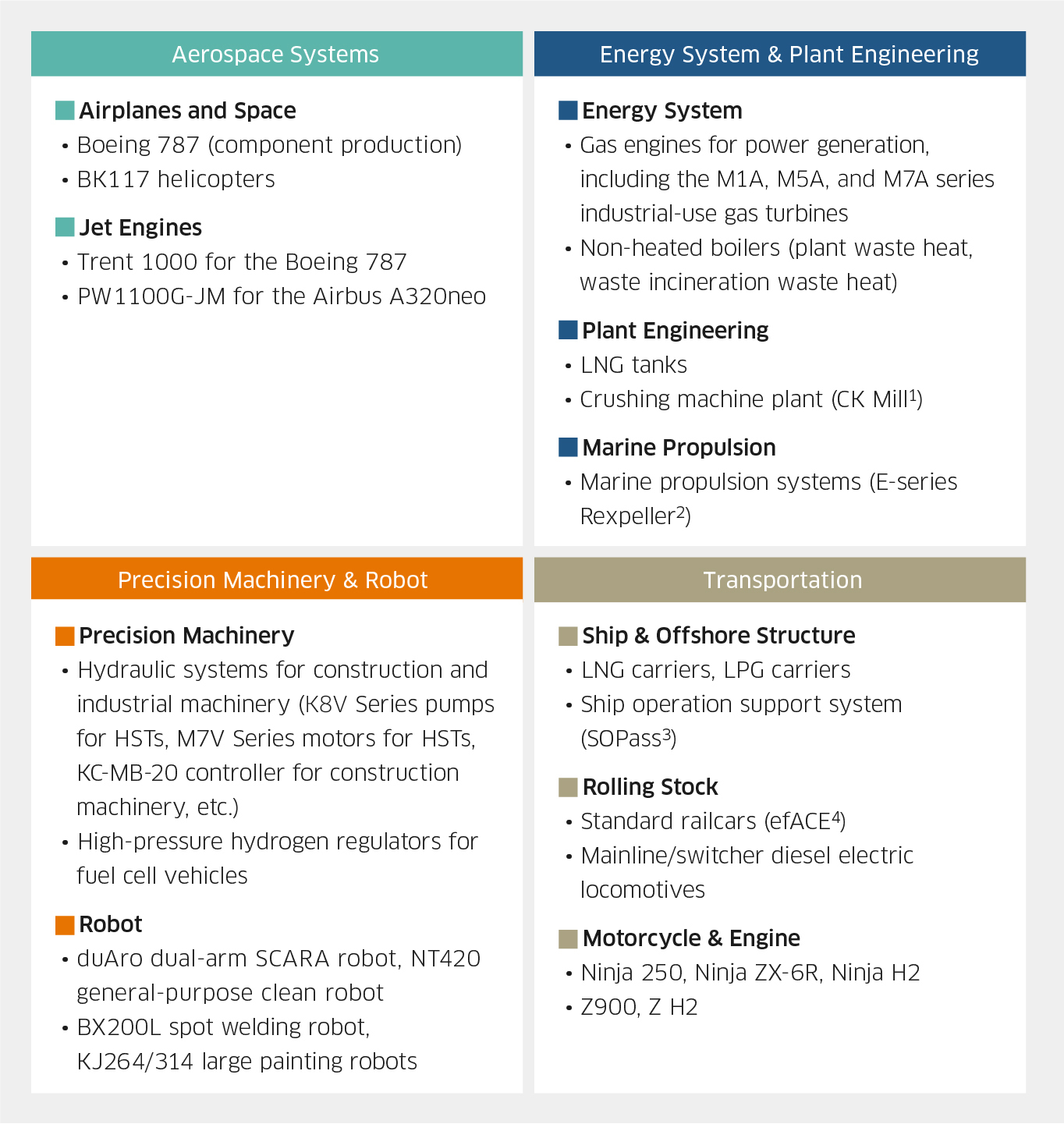
- *1 CK Mill: Named after the companies that jointly developed it, Chichibu Cement Co., Ltd. (now Taiheiyo Cement Corporation) and Kawasaki.
- *2 Developed with a focus on three Es: energy saving, easy maintenance, and environmentally friendly.
- *3 Ship Operation and Performance analysis support system
- *4 Environmentally Friendly Advanced Commuter & Express train
Particularly Notable Products That Contribute to Reducing CO2 Emissions during Use

For details on the Kawasaki Ecological Frontiers certification system for environmentally conscious products, please refer to environmentally conscious products.
External Affairs Activities Concerning Climate Change
Our Basic Stance and Structure
To contribute to realization of a society that limits the increase in the global average temperature to 1.5°C compared to pre-industrial times, the objective of the Paris Agreement, the Kawasaki Group is using its technological knowledge and expertise relating to decarbonization, actively participating in trade association activities, and contributing to the formulation of policy recommendations concerning climate change mitigation and adaptation. The Executive Officers in charge of the relevant departments ensure that trade association and public policy engagement is in line with the Group’s strategies concerning responses to climate change and report as necessary to the Board of Directors, the highest decision-making body responsible for deliberating on and finalizing fundamental sustainability policies and basic plans for the entire Group. In cases where we identify substantial misalignments between the activities of organizations of which the Group is a member and the objectives of the Paris Agreement, we engage in constructive dialogue with those organizations based on the Group’s climate change strategy and business activities, and if those misalignments cannot be eliminated after the passage of a certain period of time, we consider appropriate responses including withdrawal.
Our Structure for External Affairs Activities
At Kawasaki to date, each business segment handling an existing business or product has dealt with external affairs on its own. However, in recent years there has been an increase in the number of social issues such as the problem of global warming that should be addressed by the company as a whole. In light of this, in July 2023 we established an External Affairs & Advocacy Department in our Head Office Marketing & External Affairs Division. This is a new organization for promoting external affairs activities across the company. In collaboration with the Head Office corporate departments and each business segment, the External Affairs & Advocacy Department is pushing to build a company-wide external affairs structure. Toward the goal of realizing the Group Vision 2030, it is working to promote and strengthen our external affairs capabilities in order to create markets. Currently, even among our various projects we have positioned the issue of "climate change" in particular as one of great importance and prioritizing it in our external affairs activities.
Engagement in Public Policy and Regulations Concerning Climate Change
Hydrogen, a clean energy carrier that emit no CO2 during use, has become a focus of attention as one solution for achieving a carbon neutral society by 2050. In response, our Group has positioned the achievement of carbon neutrality centered on hydrogen electricity generation as one of the pillars of our climate change strategy and is now working to carry out that strategy in collaboration with policymakers and trade associations. Group Vision 2030, our management strategy, sets energy and environmental solutions as one of our focus fields, identifies new business including the hydrogen and large-scale CO2 capture businesses as our primary growth scenario, with the aim of achieving the 1.5°C target in line with the Paris Agreement. The hydrogen business in particular is positioned at the center of the Company’s business growth and transition plan. We are actively working on the development of rules and frameworks such as for the assessment of GHG emissions associated with the hydrogen supply chain through close cooperation with policymakers, trade associations and other stakeholders, toward achieving the objectives of Group Vision 2030 and early realization of carbon neutrality.
Initiatives with the GX Acceleration Agency
The Kawasaki Group has invested in the GX Acceleration Agency (GXA), which was established in May 2024 to accelerate the green transformation (GX) of Japan. In order to realize more than 150 trillion yen in GX investments over the next decade, the GXA will engage in such important tasks as providing financial support in the form of debt guarantees, operating carbon emissions trading systems, and collecting surcharges on fossil fuels. The Act on Promoting a Smooth Transition to a Decarbonized Growth-Oriented Economic Structure (passed May 2023) stipulates that the GXA shall be funded by the government and by the private sector, which is at the core of accelerating GX. The stance of the Japan Business Federation (Keidanren) is also to provide support. Accordingly, as a Keidanren member and as a company working to realize a carbon neutral society such as through hydrogen, the Kawasaki Group has invested in the GXA in view of the reasons for its establishment. The Kawasaki Group is contributing to the achievement of the international commitment to carbon neutrality by 2050 through its investments in the GXA—which plays a central role in accelerating green transformation throughout the country—and through a variety of alliances and activities.
Taking Part in AZEC Concept Promotion Activities
Keidanren has launched an Asia Zero Emission Community (AZEC)* Promotion Working Team to promote the realization of the AZEC concept based on public-private cooperation, and to encourage going carbon neutral in Asia. In addition, the Team will also examine policies for linking these efforts to Japan's economic growth. In sympathy with this concept and as a member of the Team, the Kawasaki Group is a participant in discussions over such matters as formulating proposals on such topics as achieving zero emissions in supply chains and building the market for green products.
- *AZEC: Comprising 11 partner countries (Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam), AZEC is a framework for cooperation on achieving carbon neutrality/net zero emissions within the region.
Development of International Rules Relating to Assessment of CO2 Emissions in Hydrogen Supply Chains
In order to promote hydrogen utilization in society, it is crucial to evaluate and demonstrate the “low-carbon nature” of hydrogen. In evaluating the GHG emissions of hydrogen to highlight its low-carbon nature, the evaluation methodology and criteria should be standardized and harmonized internationally. The Kawasaki Group is activity contributing to methodology development with relevant organizations around the world by using our accumulated technical knowledge and data concerning international liquefied hydrogen supply chains as a leading company in this field. Specifically, in May 2023, we launched a collaboration with DNV, an international third-party certification body, to establish methods of calculating CO2 emissions during maritime transportation of liquefied hydrogen. In the process, we have been accumulating knowledge about methods for performing those calculations. Furthermore, as an expert providing support to Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry, the Kawasaki Group has participated in the discussions over the methodology for determining greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from hydrogen that have taken place within the International Partnership for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells in the Economy (IPHE). We have provided technical advice, particularly with regard to those evaluations about liquefied hydrogen. Currently, Kawasaki Group members are participating as experts in an international standardization activity (ISO/TC 197/SC 1, Hydrogen at scale and horizontal energy systems working group) regarding methodologies for calculating CO2 emissions associated with hydrogen supply chains. In March 2025, international standardization of the methodologies for calculating CO2 emissions in liquefied hydrogen transport began. As an enterprise in the liquefied hydrogen businesses, the Kawasaki Group engages in the development of international standards together with related parties in Japan and abroad. These international standardization activities are collaborated with other Japanese stakeholders and are supported by the “Development of Technologies for Building a Competitive Hydrogen Supply Chain” project commissioned by Japan's New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). In addition, Yoshinori Kanehana, the Company’s Chairman of the Board, served as co-chair of the Hydrogen Council from January 2022 to June 2024. The Hydrogen Council is an organization that promotes the roles of hydrogen in the global-scale transition to alternative fuels and currently has approximately 140 members from various industries around the world. We participate in discussions on methodologies for evaluating GHG emissions with council members.
Active Contribution to Climate Change Organization
HySTRA
As a member of HySTRA (CO2-free Hydrogen Energy Supply-chain Technology Research Association), the Company participates in efforts to build a CO2-free hydrogen supply chain consisting of hydrogen production, transport/storage, and utilization, and works to establish and verify the relevant technologies to be commercialized by around 2030. The Company's role at HySTRA is to engage in building liquefied hydrogen carriers and constructing liquefied hydrogen unloading equipment and bulk storage facilities by utilizing the cryogenic technologies it has developed such as for LNG carriers, LNG storage tanks, and liquefied hydrogen tanks for rocket fuel.
JH2A
The Company has participated in the Japan Hydrogen Association (JH2A), an organization that promotes global collaboration on the hydrogen field and the formation of hydrogen supply chains, as an executive board member since its foundation in December 2020. We support the purpose of the JH2A, which is to build a hydrogen society at an early stage through the realization of social implementation projects, and by working with other member companies and organizations, national and local governments, and academia, we are promoting the “global collaboration and cross-industry, open initiatives in the hydrogen field” supported by the JH2A, thereby contributing to the development of hydrogen supply chains and a hydrogen society.
| [Related Link] |
HySE
Since its establishment in May 2023, Kawasaki Motors, Ltd. has been full member of the Hydrogen Small mobility & Engine technology Association (HySE). This research association was founded with the objective of commercializing small-sized mobility that employs hydrogen engines based on the internal combustion technologies that have been cultivated to date in Japan. HySE crosses boundaries to pull together a variety of companies such as manufacturers and suppliers in the motorcycle and automobile industries, with each contributing their knowledge. It does so not only to develop technology through research and verification, but also to engage in activities that would lead to penetration of hydrogen throughout society. Furthermore, the Kawasaki Group also participates in the HySE as a special member. Making the most of the know-how that we have cultivated as chief director of HySTRA (CO2-free Hydrogen Energy Supply-chain Technology Research Association), we will support the operation of HySE and promote initiative aimed at realizing a hydrogen society.
| [Related Link] |
Contact
If you need more information about our business,
please feel free to contact us.





