Waste to Energy Plant
Social needs for minimizing the impact and high efficiency in waste incineration has been growing recently from the standpoint of even more minimizing the impact to the environment and advancement of thermal recycling. Kawasaki meets the various needs by developing Kawasaki Advanced Stoker-type Incinerator, which has been highly developed from Stoker-type Incinerator with its credibility supported by reputation of long standing. Kawasaki has developed various systems and technologies in order to return the clean air to the environment after eliminating pollutants contained in the gas from incinerator such as hydrogen chloride(HCI), sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx). Through its extensive experience, Kawasaki provides flue gas processing system fitted to many plants as well as waste combustion system.
Advanced Stoker System
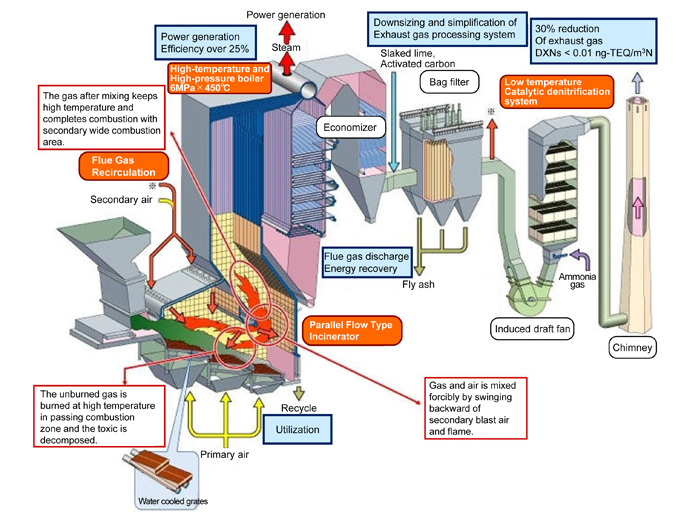
Features
Parallel flow type incinerator greatly develops the turbulent mixing of flue gas and enables low air ratio, high-temperature combustion by inverting flue gas forcibly and by installing water cooled partition ceiling in the furnace parallel to the direction waste carried. Water cooled grates save combustion loss and improves its credibility since it keeps working in case of breakage and easy maintenance by indirect water cooled structure. It enhances low air ratio, high-temperature combustion by flue gas recirculation that filtered flue gas is blown into furnace. It intends to reduce the energy loss with flue gas reduction, downsize the flue gas treatment system and minimize the formation of toxic substances.
Flue Gas Processing System
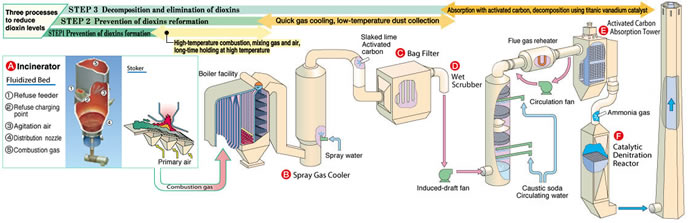
Features
- Spray Gas Cooler
Quick cooling of gas prevents the dioxin reformation.
- Bag Filter
The fly ash in flue gas, as well as the SOx and HCI that has reacted with and been absorbed by such substances as slaked lime, are eliminated when they attach to the cylindrical filtration cloth.
- Wet Scrubber
Hydrogen chloride and sulfur oxides, as well as mercury, are removed from the flue gas. By the reheater, white plumes can be prevented.
- Activated Carbon Absorption Tower
Discharge the dioxin in the flue gas absorbed in activated carbon. Activated carbon charged from the upper part of the tower is moved down periodically and discharged at the bottom of packed bed.
- Catalytic Denitration Reactor
Besides removing the nitrogen oxide contained in flue gas as nonpolluting nitrogen and water by blowing ammonia gas and catalyst, dioxin can be decomposed and removed.
Contact
If you need more information about our business,
please feel free to contact us.





