| |
Tokyo, Sep. 7, 2006—Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (KHI) today issued its new medium-term business plan, Global K, covering the period from FY2006, ending March 31, 2007, to FY2010. In this plan, the Company aims to further enhance strategies and measures set in the previous K21 Medium-Term Business Plan, under which it established a stable earnings structure. Having decided on its corporate vision and what each business should be 10 years in the future, KHI has set the Global K plan to guide the next five years, with a view to achieving its vision. The plan will be reviewed at its halfway point in FY2008, reflecting its progress.
| 1. |
Corporate Vision: |
| |
Enriching lifestyles and helping safeguard the environment:
Global Kawasaki |
| |
KHI aims to become a leading global enterprise that enriches lifestyles and helps safeguard the environment through its businesses, which encompass land, sea, and air transportation systems, and the energy and environmental engineering sectors. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Basic Objectives: |
| |
The Company should leap forward to become a highly profitable, globally recognized enterprise during the period of the Global K plan by implementing the principal management policies of “Quality Followed by Quantity,” selectivity and concentration, and stronger non-price competitiveness. |
| |
| (1) |
Implement ongoing reforms to establish a sustainable growth cycle. |
| (2) |
Achieve steady growth in keeping with the Global Kawasaki vision. |
| (3) |
Build a solid Kawasaki brand by leveraging consumer trust. |
| (4) |
Reinforce CSR organization to enhance Corporate Quality. |
|
| |
|
| 3. |
Gist of the Plan: |
| |
| (1) |
What Each Business Should be 10 Years in the Future: |
| |
 |
Rolling Stock: a world-class maker of rolling stock systems that draw on top technologies and quality |
 |
Aerospace: a leader in Japan’s aerospace industry, with solid competitiveness internationally in aircraft manufacturing |
 |
Gas Turbines & Machinery: a prime mover manufacturer with world-class technologies in the transportation equipment and energy fields |
 |
Consumer Products & Machinery: a leisure vehicle and engine manufacturer with a top brand recognized for high quality and high performance |
 |
Energy & Environmental Engineering: a global leader in energy and environmental engineering with a reputation built on superb, proprietary technologies |
 |
Industrial Robots: a world-leading industrial robot manufacturer with a reputation built on key and systems technologies for high-performance and multifunctional robots |
 |
Shipbuilding: a shipbuilder with world-class profitability that draws on advanced technologies and Chinese production sites to withstand market swings |
 |
Industrial Hydraulic Products: one of the world’s top five hydraulic equipment makers, with outstanding technologies and product quality |
|
| |
|
| (2) |
Selectivity and Concentration: |
| |
| 1) |
Positioning of the Businesses |
| |
 |
Four Core Businesses: Rolling Stock, Aerospace, Gas Turbines & Machinery, and Consumer Products & Machinery—should be operating globally as earnings drivers of the KHI Group. |
 |
Developing Business: Energy & Environmental Engineering—should be nurtured as a new earnings driver of the Group by implementing various measures including reorganization of the business and M&A. |
 |
Self-sufficient Businesses: Industrial Robots, Shipbuilding, and Industrial Hydraulic Products—should be established as a specialist in each business field and secure stable earnings. |
|
| |
|
| 2) |
Positioning of Business Units/Products |
| |
 |
Accelerate selectivity and concentration of BUs/products judging from their competitive, technological and other advantages, and the possibility of improving profitability. |
 |
Classify BUs/products into four categories: Priority businesses, developing businesses, businesses with stable earnings, and businesses requiring structural reform. Priority businesses and developing businesses will receive weighted management resources. |
 |
Policies for the businesses requiring structural reform will be decided after examining their importance and positioning in the medium term vis-a-vis their market environment, the possibility of profitability improvement, and strategic value for the KHI Group. |
|
|
| |
|
| (3) |
Plans for Allocation of Management Resources: |
| |
| 1) |
Capital investment plan |
| |
 |
Invest ¥300 billion over five years, or ¥60 billion annually. |
 |
Invest ¥13 billion more annually than the average annual cost base for the past three years, which was ¥47 billion.
|
|
| |
|
| 2) |
R&D investment plan |
| |
 |
Invest ¥200 billion over five years, or ¥40 billion annually. |
 |
Invest ¥13 billion more annually than the average annual cost base for the past three years. |
|
| |
|
| 3) |
Personnel plan |
| |
To compensate for the increased number of employees at mandatory retirement age and to meet the Company’s expansion plans: |
| |
 |
Hire 5,000 people over five years, or 1,000 people annually. |
 |
Increase employee numbers to 31,000 at FY2010 year-end, an increase of 2,000 from FY2005 year-end. |
|
|
| |
|
| (4) |
Priority Initiatives: |
| |
| 1) |
Strengthen technological capabilities |
| |
With renewed awareness that technology is a key source of earnings, reinforce technological development capabilities, production technology capabilities, and intellectual asset strategies. |
| |
|
| 2) |
Encourage market-oriented thinking and action |
| |
Become more market-focused to strengthen non-price competitiveness. Keep in mind that profits are generated from the market. All thinking and action in all processes of business operations should stem from the market. |
| |
|
| 3) |
Accelerate global business development |
| |
Aimed at future growth, accelerate global business development in sales, production and procurement, and cooperate with partner companies. |
| |
|
| 4) |
Create and cultivate new products and businesses |
| |
Cultivate next-generation core businesses throughout the Global K period by overhauling technologies and creating new businesses fulfilling high-priority social needs. |
| |
|
| 5) |
Strengthen Group management capabilities |
| |
While maintaining the advantages of the internal company system of management efficiency and flexibility, reinforce Companywide strategy development and Group management/oversight functions at headquarters aimed at increasing the centripetal force of the KHI Group and harmonizing the optimization of the Company’s individual parts and the Group as a whole.
Create a smaller, stronger and more agile headquarters, and selectively reinforce the operations of subsidiaries and affiliates. |
| |
|
| 6) |
Promote CSR |
| |
Improving management quality by promoting CSR |
| |
 |
Enhance internal control systems and compliance |
 |
Increase management transparency |
 |
Strengthen risk management capabilities |
 |
Endorse environment-friendly business operations |
|
|
|
| |
|
| 4. |
Quantitative Targets: |
| |
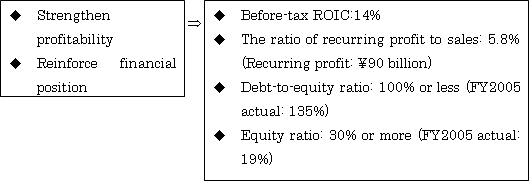
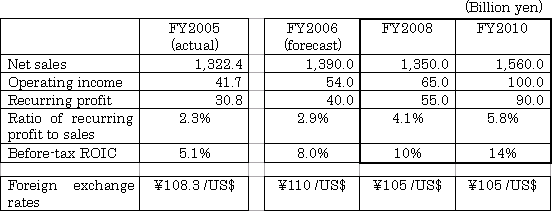
During the period of the Global K plan, the KHI Group should improve ROIC and the ratio of recurring profit to sales.
Notes
Recurring profit: the sum of operating income, net interest income (expenses), dividend income, and other non-operating but recurring items.
Before-tax ROIC: earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) divided by invested capital.
Debt-to-equity ratio: ratio of interest-bearing debts against total shareholders’ equity.
Note
Actual differences stemming from a change in accounting for retirement benefits and severance costs (approx. ¥13 billion) will be completely amortized in FY2009.
 |
Shareholder returns |
| |
 |
Gradually increase dividends in line with improved profitability. |
 |
Medium- to long-term target of payout ratio: 30%, based on financial projections and the progress of businesses in the plan. |
|
|
|







