Kawasaki Develops New Moss-type Tank for LNG Transport Vessels, Obtains AIPs from Three Key Organizations
Jun. 05, 2017
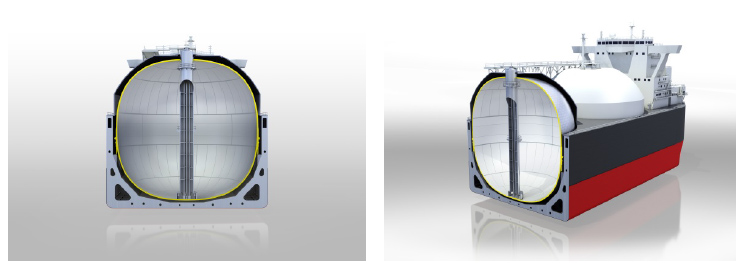
Tokyo, June 5, 2017 — Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. announced today that it has obtained approval in principle (AIP) from Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK), the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) and DNV GL*1 for the new Moss-type liquefied natural gas (LNG) fuel storage tank it developed for LNG transport vessels.*2 The AIPs from these three organizations, which boast some of the best technological capabilities and wide-reaching experience of all major classification organizations worldwide, give testament to the high trustworthiness and practical applicability of Kawasaki's new Moss-type LNG tank.
LNG marine shipping volumes have been increasing rapidly in recent years in response to growing demand for the fuel's use in electric power generation. As a result, there is a rising need for LNG carriers designed to enable navigation of the newly expanded Panama Canal while also providing higher loading capacities for improved shipping efficiency.
Compared with common spherical Moss-type tank designs, Kawasaki's newly approved Moss-type tank has been modified so that its vertical cross section assumes a more square shape, reducing gaps between the ship's hull and the tank. This preserves the excellent anti-sloshing performance and ease of inspection during tank construction and ship transport operations seen in standard Moss-type tanks while providing a boost to volumetric efficiency.
The main advantages of the new Moss-type LNG tank are as follows:
- ●
- It offers roughly 15% additional storage capacity compared with the spherical tanks installed on existing 155,000 m3 LNG carriers, without the need for increased tank width or height. The new design enables the development of LNG carriers with a storage capacity of 180,000 m3 and capable of navigating the newly expanded Panama Canal.
- ●
- Tank height has been kept lower than existing stretched spherical tanks*3 to enable improved field of vision from the ship's bridge and better recovery of ship balance (ability of the vessel to return to its original orientation after tilting).
- ●
- Just like existing Moss-type tanks, this new LNG tank is classified as a type B independent tank by the IMO.*4 A high-precision structural analysis approach, utilizing a newly devised strength evaluation method*5 based on the traditional structural analysis approach, is employed to ensure high reliability for the new tank design.
- ●
- The tank's aluminum-alloy panels form spherical walls, minimizing sloshing caused by ship movement and thus eliminating the need for loading limitations.
- ●
- The design facilitates ease of inspection during construction and ship transport operations, resulting in higher safety performance.
- ●
- The new tank is compatible with the Kawasaki Panel System, an insulation system offering world-leading performance designed using proprietary Kawasaki technologies. Integration of the Kawasaki Panel System reduces boil-off gas (BOG) to mitigate LNG loss during transport operations.
Moving forward, Kawasaki will continue pursuing research and development in LNG and other liquefied gas transport vessels as it strives to produce highly reliable and safe products with excellent transport efficiency, all in an effort to contribute toward the energy transport industries both in Japan and abroad.
*2 Moss-type LNG tank: A spherical tank independent from the ship hull, supported by a cylindrical structure known as a "skirt."
*3 Stretched spherical tank: A spherical tank in which a cylindrical section has been added to the equatorial area to increase internal capacity.
*4 IMO-classified type B independent tank: One type of liquefied gas storage tank classification used by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). This type features a partial secondary barrier to prevent leakage of tank contents.
*5 A strength evaluation method developed based on advice from experts via the "New LNG Transport Vessel Design-strength Evaluation Method Investigation for Establishment of a Shale Gas Marine Transport Framework" commissioned by the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT)

Contact
If you need more information about our business,
please feel free to contact us.





